Pregnancy is a miraculous journey, but it comes with its share of challenges, one of them being Gestational Diabetes. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of pregnancy-related diabetes, exploring its types, causes, impact, and management.
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Pregnancy Diabetes
Pregnancy diabetes, or gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy. It affects how the body uses insulin, the hormone responsible for converting sugar, starches, and other food into energy. While it usually resolves after childbirth, it requires careful management to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
B. Importance of Awareness
Awareness about pregnancy diabetes is crucial for expectant mothers to navigate this phase successfully. Understanding the risks, symptoms, and management strategies empowers women to make informed decisions for a healthy pregnancy.
II. Types of Pregnancy Diabetes
A. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is the most common form, emerging during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands. This condition requires vigilant monitoring and often involves lifestyle adjustments and, in some cases, medication.
B. Pre-existing Diabetes during Pregnancy
Some women enter pregnancy with pre-existing diabetes, either type 1 or type 2. Managing diabetes during pregnancy poses unique challenges, necessitating a collaborative approach between the woman, her healthcare team, and specialists.
III. Causes and Risk Factors
A. Hormonal Changes
The hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can interfere with insulin effectiveness, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Grasping these changes is essential for managing them effectively.
B. Genetic Predisposition
Having a family background of diabetes raises the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Genetic factors play a significant role, emphasizing the importance of early screenings for at-risk individuals.
C. Obesity and Lifestyle
Overweight or obese women are more susceptible to gestational diabetes. Embracing a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and regular exercise, can significantly reduce these risks.
IV. Symptoms and Diagnosis
A. Common Signs of Pregnancy Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms is key to early diagnosis. Increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue are common indicators that warrant further investigation.
B. Screening and Diagnostic Tests
Prenatal screenings, including glucose tolerance tests, are essential for identifying gestational diabetes. Identifying the issue early enables prompt intervention and effective management.
V. Impact on Mother and Baby
A. Maternal Health Complications
Uncontrolled gestational diabetes can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, increased likelihood of C-section delivery, and an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
B. Fetal and Neonatal Risks
Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may face challenges like macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia after birth, and a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes.
VI. Management and Treatment
A. Dietary Changes
A balanced diet, focusing on controlled carbohydrate intake, is a cornerstone of managing gestational diabetes. Consulting with a nutritionist can help create a customized meal plan.
B. Medication and Insulin Therapy
In some cases, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to maintain blood sugar levels within the target range. Close monitoring is crucial to adjust treatment as needed.
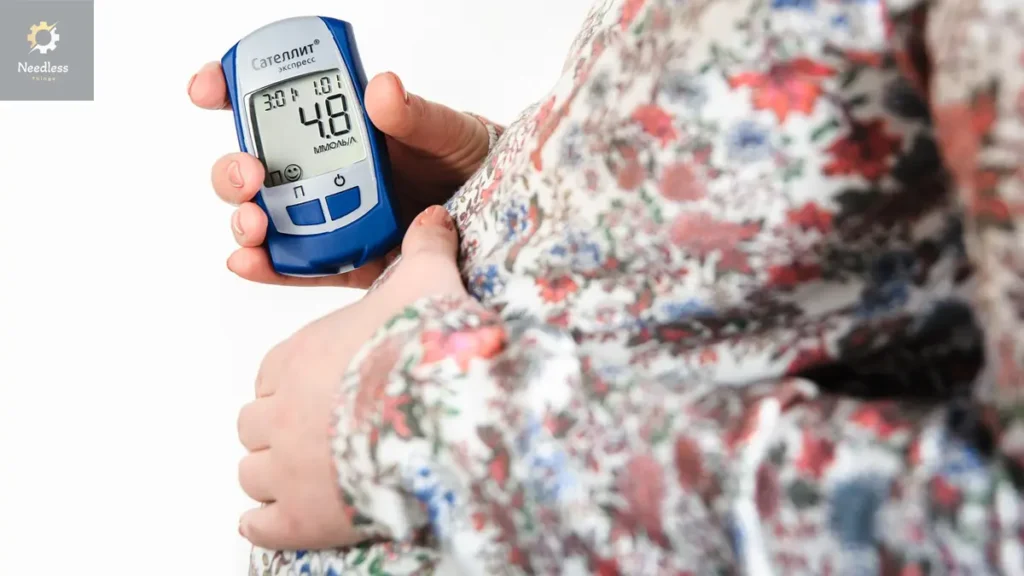
C. Regular Monitoring
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is essential to track changes and ensure timely adjustments to the treatment plan. This proactive approach is vital for a healthy pregnancy outcome.
VII. Lifestyle Modifications
A. Importance of Exercise
Regular physical activity, tailored to an individual’s health status, helps control blood sugar levels. Consultation with healthcare providers ensures safe and effective exercise during pregnancy.
B. Weight Management
Keeping a balanced weight lowers the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes. A combination of a balanced diet and appropriate exercise supports overall well-being.
VIII. Prevention Strategies
A. Prenatal Care
Early and consistent prenatal care is foundational in preventing complications. Regular check-ups and screenings allow for proactive intervention if gestational diabetes develops.
B. Healthy Lifestyle Practices
Embracing a healthy lifestyle before and during pregnancy significantly reduces the risk of gestational diabetes. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress.
IX. The Role of Healthcare Professionals
A. Obstetricians
Collaboration between obstetricians and other healthcare professionals is crucial for comprehensive care. Regular check-ups, screenings, and monitoring support the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
B. Endocrinologists
In cases of pre-existing diabetes during pregnancy, endocrinologists play a vital role in managing and optimizing blood sugar control. Their expertise ensures a coordinated approach to maternal-fetal health.
X. Emotional and Psychological Impact
A. Coping with Diagnosis
Receiving a gestational diabetes diagnosis can be emotionally demanding. Providing emotional support and resources to cope with stress and anxiety is integral to holistic care.
B. Support Systems
Building a strong support system, including friends, family, and healthcare providers, aids in navigating the emotional and physical aspects of managing gestational diabetes.
XI. Real-life Stories
A. Personal Experiences
Hearing real-life stories from women who have successfully managed gestational diabetes provides inspiration and valuable insights for those currently facing similar challenges.
B. Success Stories
Highlighting success stories emphasizes that with proper management and support, women with gestational diabetes can have healthy pregnancies and deliver healthy babies.
XII. Myths and Facts
A. Dispelling Misconceptions
Dispelling common myths surrounding gestational diabetes fosters accurate understanding. Addressing misconceptions ensures that women receive reliable information for informed decision-making.
B. Common Beliefs about Pregnancy Diabetes
Exploring prevalent beliefs about pregnancy diabetes helps challenge stereotypes and encourages open conversations about this common condition.
XIII. Global Statistics and Trends
A. Prevalence Rates
Examining global statistics sheds light on the prevalence of gestational diabetes, emphasizing the need for widespread awareness and preventive measures.
B. Geographical Variances
Understanding regional variations in gestational diabetes rates enables targeted interventions and tailored healthcare strategies.
XIV. Research and Innovations
A. Ongoing Studies
Highlighting current research initiatives provides a glimpse into the evolving landscape of gestational diabetes management and prevention.
B. Future Prospects
Exploring potential future innovations fosters hope for improved strategies, treatments, and preventive measures against gestational diabetes.
Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
Understanding pregnancy diabetes is vital for expectant mothers and healthcare professionals alike. By recognizing its impact, causes, and management strategies, we empower women to navigate this phase with confidence.
B. Encouraging Awareness
Raising awareness about gestational diabetes is a collective responsibility. By sharing knowledge and fostering a supportive environment, we contribute to healthier pregnancies and brighter futures for both mothers and babies.
FAQs: Understanding Pregnancy Diabetes
Is gestational diabetes common?
- Gestational diabetes is relatively common, affecting around 6-9% of pregnancies.
Can gestational diabetes be prevented?
- While not always preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle before and during pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk.
What is the long-term impact of gestational diabetes on the mother?
- Mothers with gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
How does gestational diabetes affect the baby?
- Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may have a higher risk of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Can gestational diabetes be managed without medication?
- In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may be sufficient, but medication or insulin therapy is sometimes necessary for optimal management.